This packages combines data collected as part of an MSc. Thesis Project. The goal of this project was to build an openly accessible database with data from the top ranked universities of each African country. The project is supported by the Global Health Engineering group at ETH Zurich, Switzerland.

Installation
You can install the development version of universityrankingafrica from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("openwashdata/universityrankingafrica")Alternatively, you can download the individual dataset as a CSV or XLSX file from the table below.
| dataset | CSV | XLSX |
|---|---|---|
| ranking | Download CSV | Download XLSX |
| african_countries | Download CSV | Download XLSX |
MSc. Thesis Project
Description
Data from institutional and national levels was combined into a dataset to provide a comprehensive characterization of the top ranked Universities of every African country. This was done to demonstrate the correlation of certain attributes with the academic ranking performance. The dataset also highlights the difficulties of accessing data from many African Universities online.
Research Question
Which attributes of an African university correlate with its performance in an international ranking?
Data
The data was collected between April and June 2023 using only the official websites of the Universities. The ranking data originates from the Ranking Web of Universities. It’s worth noting that while the World Ranking comprises 11’997 universities, the African Ranking accounts for 2’064 universities. For the data collection at hand, it was decided to only consider the 3 (at most) highest ranked universities of each African country. The gathered data offers interesting insights into the African academic landscape, mostly through the process of combing through more than 140 websites in the search for information. Generally, this data collection process gets more and more difficult the further down the ranking performance goes: Navigation is more confusing and useful information scarcer. Assisting institutions in improving the quality of their web contents could be one possible avenue for cooperation with African universities in the future.
The package provides access to two data sets.
library(universityrankingafrica)The ranking data set has 26 variables and 141 observations. For an overview of the variable names, see the following table.
ranking | variable_name | variable_type | description |
|---|---|---|
| university | string | Name of the University |
| country | drop-down from List of African countries | Country where the University is located |
| city | string | City where the University is located |
| ror_entry_correct | y / n | Is the entry on the ror.org-website corresponding to the University correct? In most “n”-cases, the stated website is incorrect |
| url | URL | Official website of the University |
| website_secure | y / n | Does the website use https? Is there no security related pop-up upon opening the website? |
| website_up_to_date | y / n | Are news articles on the website up to date OR is the copyright date of the website the current year? |
| website_function | good / medium / poor / defunct | Good: navigating through the website is smooth, no OR very few dead or redundant links. Medium: some dead links within the webpage, some placeholders (“lorem ipsum”) still visible, some blank or empty pages. Poor: Navigating through the website is very difficult. Defunct: the official link of the university’s website is no longer hosted, or is otherwise inaccessible. Note: Does NOT indicate how much information can be found on the website. |
| website_language | string | Default language of the landing site |
| colonial_power | string | The colonial Power from which the country gained independence, if it ever was colonized or became independent. |
| rank_africa | int | The rank of the University in Africa (2’064 universities), according to https://www.webometrics.info/en/Ranking_africa |
| rank_world | int | The rank of the University in the World (11’997 universities), according to https://www.webometrics.info/en/Ranking_africa |
| impact_rank | int | The impact rank of the University, according to https://www.webometrics.info/en/Ranking_africa |
| openness_rank | int | The openness rank of the University, according to https://www.webometrics.info/en/Ranking_africa |
| excellence_rank | int | The excellence rank of the University, according to https://www.webometrics.info/en/Ranking_africa |
| academic_system | American / French | Which academic system is used at the University: American (Undergraduate, Graduate, Doctorate) or French (LMD: Licence, Master, Doctorat) |
| engineering_courses | int | The number of different undergraduate engineering courses the University offers. |
| years_of_study | int | Stated duration of an undergraduate engineering degree. If the University doesn’t offer engineering degrees, the duration of another undergraduate degree is indicated. |
| online_application | y / n | Is there a possibility to apply for the University online? If no explicit method is stated to send the application online, it’s considered as “no” |
| international_students | y / n | Does the University give special information to interested foreign students on how to enter? |
| yearly_fee | int | Required yearly tuition fee for a local student to complete a year of an undergraduate engineering degree at the University. If the University doesn’t offer engineering degrees, the general tuition fee is indicated |
| masters_programme | y / n | Does the University offer Master’s programmes? (NOT only engineering) |
| online_payment | y / n | Is there a possibility to pay University fees online? (either banking information, instructions or a direct link) |
| number_of_students | int | If stated on the website, the number of students studying at the University |
| access_date | date (dd.mm.yyyy) | Date the University website was accessed |
| remarks | string | Personal notes on the University |
The african_countries data set has 7 variables and 55 observations. For an overview of the variable names, see the following table.
african_countries| variable_name | variable_type | description |
|---|---|---|
| countries | string | Name of the Country |
| region | string | African Region where the Country is located |
| uni_count | int | Number of Universities in the corresponding country |
| best_uni_rank | int | Rank Africa of the best University of the country |
| gdp | int | GDP of the country in 2021 (With a few exceptions for which the data is older). Source: ourworldindata.org, World Bank, international-$ in 2017 prices (accounting for differences in cost of living) |
| gdp_per_capita | int | GDP per Capita of the country in 2021 (With a few exceptions for which the data is older). Source: ourworldindata.org, World Bank, international-$ in 2017 prices (accounting for differences in cost of living) |
| hdi | double between 0 and 1 | Human Development Index of the country in 2021. Source: ourworldindata.org, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Variable time span: 1990-2021. Higher number means better developped. |
Example
1) Mapping Countries with the Best-Ranked Universities
The code below demonstrates how to create a map in R that highlights countries hosting the top-ranked universities. This method involves picking the best university in each country and associating its rank with that specific country.
library(universityrankingafrica)
library(tidyverse)
library(sf)
library(rnaturalearth)
top_ranked_per_country <- african_countries |>
select(countries, best_uni_rank)
world <- ne_countries(scale = "medium", returnclass = "sf")
africa_map <- left_join(world,
top_ranked_per_country, by = c("name_long" = "countries")) |>
filter(continent == "Africa")
ggplot() +
theme_void() +
geom_sf(data = africa_map, aes(fill = best_uni_rank), color = "white", lwd = 0) +
scale_fill_gradientn(name = paste("Rank Africa", "\n(out of 2'064)"),
trans = "log",
labels = scales::label_number(accuracy = 1),
colors = c("#2E8B57","#9DBF9E", "#FCB97D", "#A84268"),
na.value = "grey80",
guide = guide_colorbar(title.position = "top", title.vjust = 1.5)) +
labs(title = "Top-Ranked Universities in Africa",
subtitle = "Comparison of the Highest-Ranked University in each African Country",
caption = "Source: Ranking Web of Universities (https://www.webometrics.info/en/Africa)") +
theme(legend.position = c(-0.1, 0.3), legend.direction = "horizontal",
plot.title = element_text(size = 20, hjust = 0, vjust = 0),
plot.subtitle = element_text(size = 10, hjust = 0, vjust = 0.5),
plot.caption = element_text(size = 10, color = "darkgray", hjust = -0.6)) +
coord_sf(ylim = c(-40, 40))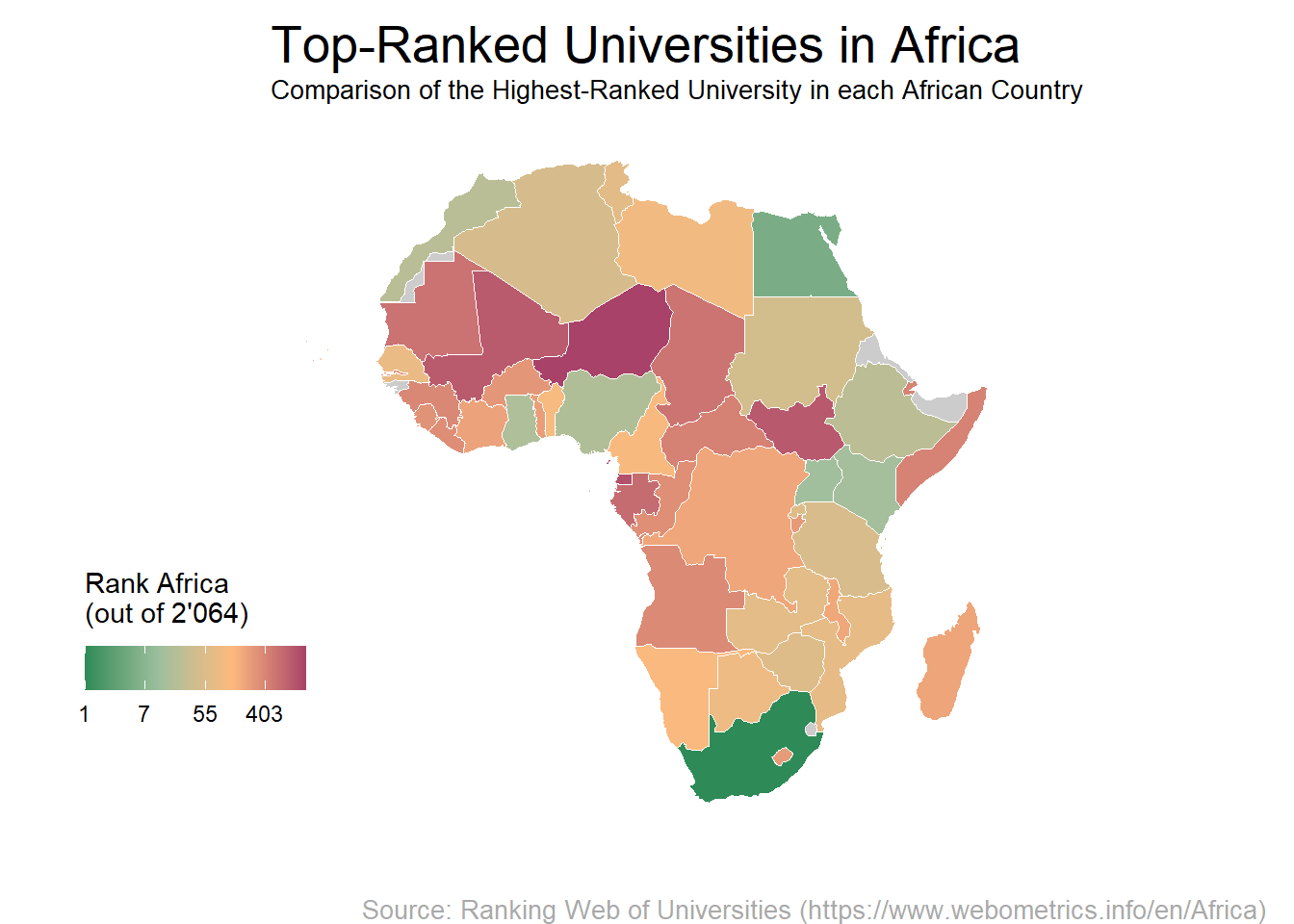
2) Exploring Colonial’s Legacy on African University Ranking
This analysis investigates whether a correlation exists between the colonial power that previously governed African nations and their current university rankings.
library(universityrankingafrica)
library(tidyverse)
library(broom)
data <- ranking |>
filter(colonial_power %in% c("United Kingdom", "France", "Belgium", "Italy", "Portugal"))
# Create a scatter plot
ggplot(data, aes(x = colonial_power, y = rank_africa)) +
geom_point() +
labs(x = "Colonial Power at Independence", y = "Africa Rank") +
ggtitle("University Ranking in Africa vs Colonial Power at Independence")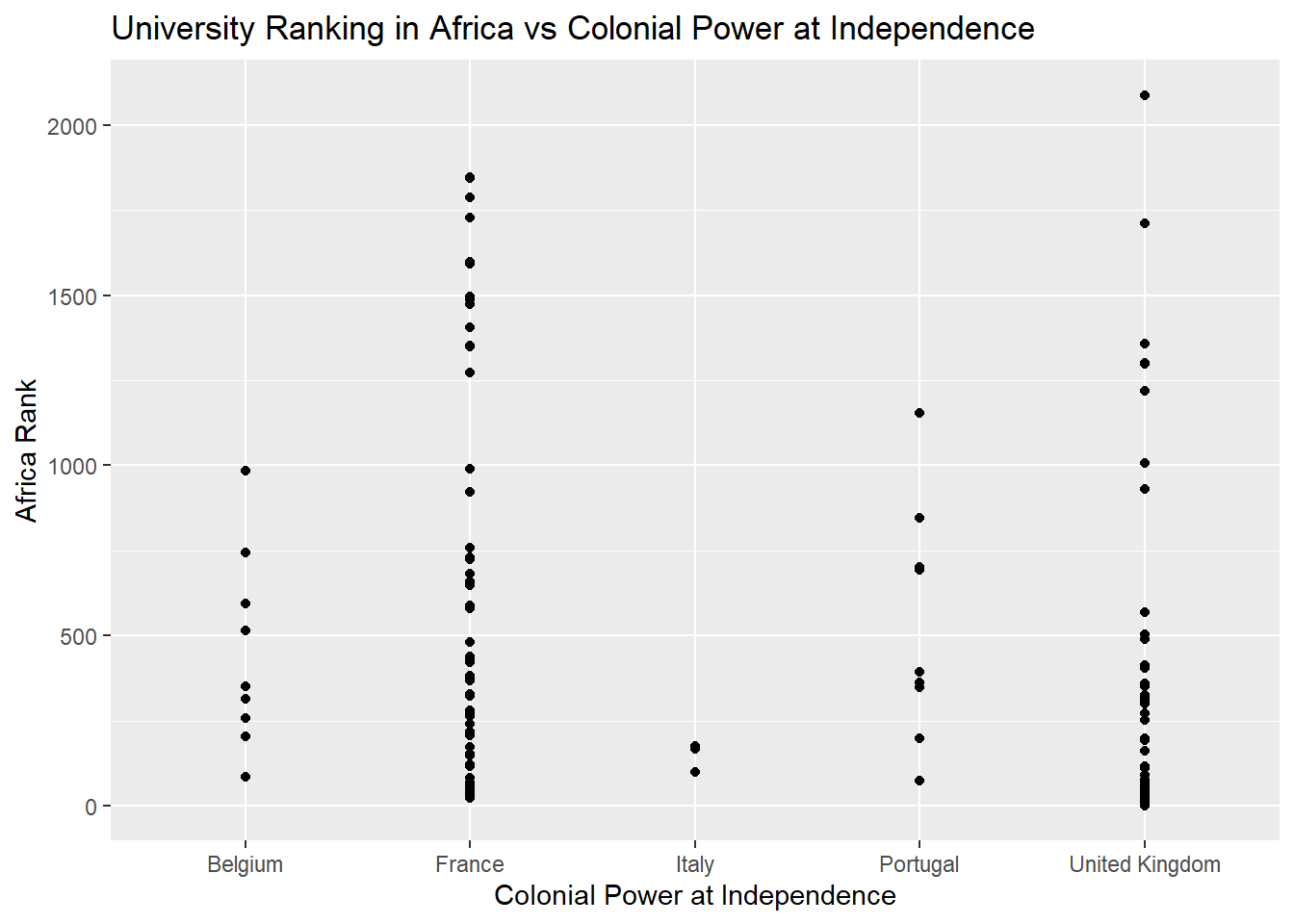
# Perform linear regression
model <- lm(rank_africa ~ colonial_power, data = data)
print(tidy(model))
#> # A tibble: 5 × 5
#> term estimate std.error statistic p.value
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 (Intercept) 449. 168. 2.68 0.00834
#> 2 colonial_powerFrance 201. 182. 1.11 0.271
#> 3 colonial_powerItaly -302. 335. -0.900 0.370
#> 4 colonial_powerPortugal 80.3 237. 0.339 0.735
#> 5 colonial_powerUnited Kingdom -117. 181. -0.646 0.519
print(summary(model)$r.squared)
#> [1] 0.0895955Interpretation
The model doesn’t provide strong evidence that the specific colonial powers (France, Italy, Portugal, United Kingdom) significantly predict the university rankings in Africa based on their p-values which are greater than conventional thresholds like 0.05.. The low R-squared value indicates that the model might not explain much of the variability in the university rankings, suggesting that factors beyond colonial power might influence these rankings significantly.
License
Data are available as CC-BY.
Citation
To cite this package, please use:
citation("universityrankingafrica")
#> Um Paket 'universityrankingafrica' in Publikationen zu zitieren, nutzen
#> Sie bitte:
#>
#> Sigrist S, Skorik S (2023). "universityrankingafrica: University
#> Ranking Africa."
#>
#> Ein BibTeX-Eintrag für LaTeX-Benutzer ist
#>
#> @Misc{sigristskorik,
#> title = {universityrankingafrica: University Ranking Africa},
#> author = {Samuel Sigrist and Sophia Skorik},
#> year = {2023},
#> abstract = {Data from institutional and national levels was combined into a dataset to provide a comprehensive characterization of the top ranked Universities of every African country. This was done to demonstrate the correlation of certain attributes with the academic ranking performance. The dataset also highlights the difficulties of accessing data from many African Universities online.},
#> version = {0.0.0.9000},
#> }